Understanding GLP-1 Mechanisms
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin hormone naturally produced by intestinal L-cells. Research shows it plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis and has significant implications for weight management studies.
GLP-1 receptor agonists are synthetic analogs that mimic natural GLP-1 but with enhanced stability and extended half-life, making them valuable tools for metabolic research.
Primary Research Mechanisms:
- Appetite suppression and satiety signaling
- Glucose-dependent insulin secretion
- Delayed gastric emptying
- Glucagon suppression
- Central nervous system appetite control
Featured Research Studies
Cutting-edge research on GLP-1 peptides and weight management

Semaglutide Weight Reduction Studies
Multiple randomized controlled trials have demonstrated significant weight loss effects with once-weekly semaglutide administration. Studies show average weight reductions of 12-15% over 68 weeks.
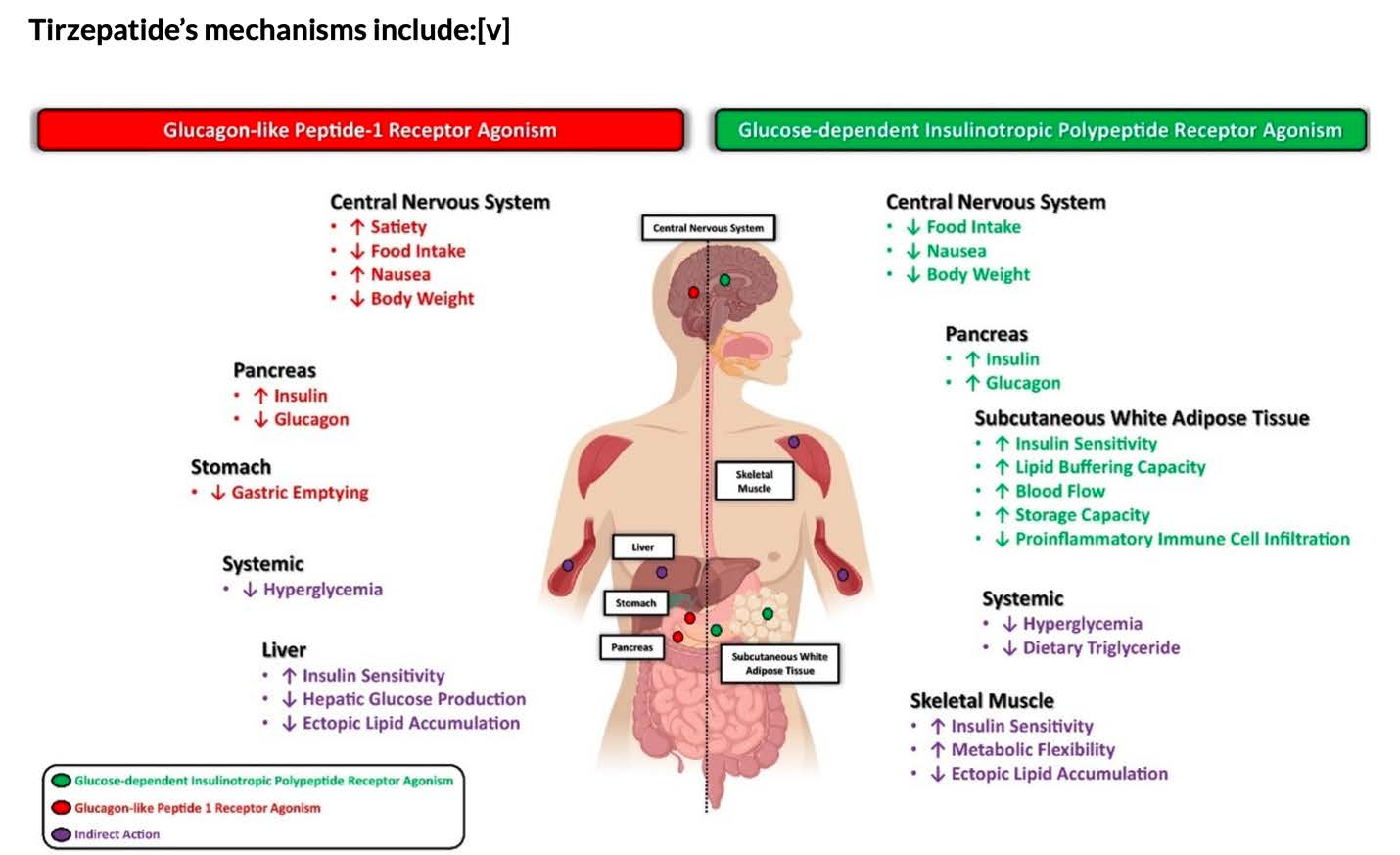
Tirzepatide Dual-Action Research
Research on tirzepatide's dual GLP-1/GIP receptor activation shows enhanced weight loss compared to single agonists, with some studies reporting up to 20% weight reduction.

Retatrutide Triple-Agonist Trials
Emerging research on retatrutide's triple-receptor targeting (GLP-1/GIP/Glucagon) demonstrates unprecedented weight loss effects, with preliminary studies showing 24% weight reduction.

Combination Therapy Studies
Research combining GLP-1 agonists with other peptides shows enhanced satiety effects and improved weight loss outcomes through complementary mechanisms.
Research Success Stories

Clinical Trial Results
Documented transformations from clinical research studies demonstrate the efficacy of GLP-1 interventions.

Measurable Outcomes
Research demonstrates consistent and measurable weight loss across diverse study populations.

Progressive Results
Studies show progressive weight loss over time with sustained GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy.
Mechanisms of Action
Understanding how GLP-1 peptides work at the cellular level
Central Nervous System Effects
- Hypothalamic Action: Activates neurons in appetite control centers
- Reward Pathways: Modulates food reward and craving mechanisms
- Satiety Centers: Enhances fullness signals and portion control
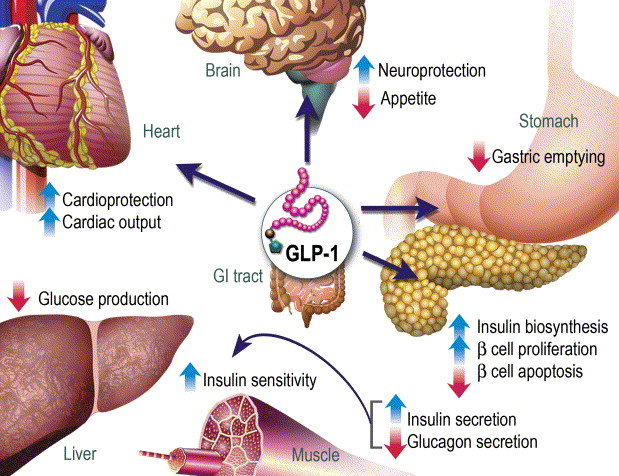
Peripheral Mechanisms
- Gastric Effects: Delays gastric emptying, prolonging satiety
- Beta Cell Function: Enhances insulin secretion
- Metabolic Impact: Improves insulin sensitivity
Current Research Applications

Metabolic Studies
- • Energy expenditure measurement
- • Metabolic rate assessment
- • Substrate utilization analysis
- • Thermogenesis research
- • Brown adipose tissue activation
Cardiovascular Research
- • Cardiovascular risk factor analysis
- • Blood pressure regulation studies
- • Endothelial function research
- • Inflammatory marker reduction
- • Cardiac protection mechanisms
Molecular Research
- • Receptor binding affinity studies
- • Signal transduction pathways
- • Gene expression profiling
- • Protein-protein interactions
- • Pharmacokinetic analysis
Research Tools & Resources
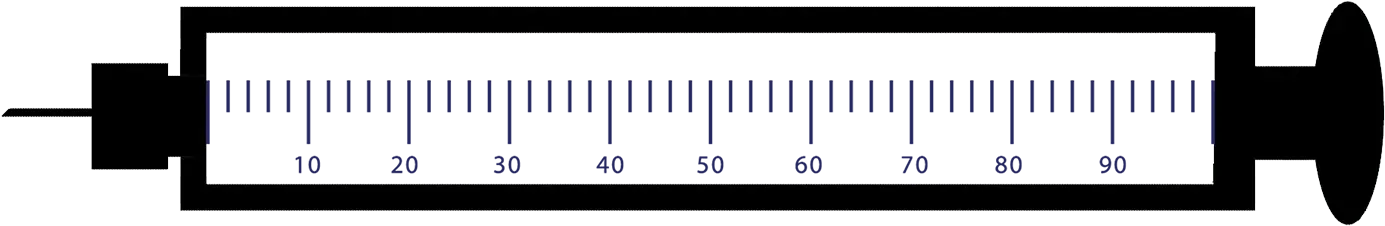
Peptide Calculator
Calculate precise concentrations for your GLP-1 research protocols. Essential for accurate dosing and consistent results.
- Concentration calculations
- Volume conversions
- Visual dosing guides
Comprehensive Peptide Database
Access detailed information on GLP-1 peptides and many other research compounds including healing peptides, growth factors, and specialty peptides.
- GLP-1, healing, and specialty peptides
- Molecular structures & properties
- Research references & protocols
Frequently Asked Research Questions
What makes tirzepatide different from semaglutide in research?
Tirzepatide is a dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist, while semaglutide targets only GLP-1 receptors. Research shows tirzepatide may produce greater weight loss (15-20% vs 12-15%) due to its dual mechanism targeting both incretin systems. The GIP component may enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation beyond GLP-1 alone.
How should GLP-1 peptides be stored for research applications?
Store lyophilized peptides at -4°F in a dry environment. Once reconstituted with bacteriostatic water, refrigerate at 35-46°F and use within 60 days for optimal stability. Always use sterile technique and handle in a clean research environment.
What is the significance of retatrutide being a triple agonist?
Retatrutide targets GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors simultaneously. This tri-agonist approach may offer superior weight loss and metabolic benefits by addressing appetite (GLP-1), insulin sensitivity (GIP), and energy expenditure (glucagon) pathways. Early research suggests up to 24% weight loss, surpassing dual agonists.
Why is peptide purity important in GLP-1 research?
High purity (99%+) ensures consistent research results and accurate dose-response relationships. Impurities can affect receptor binding, alter pharmacokinetics, and introduce variables that compromise research validity. Our peptides undergo rigorous testing to guarantee research-grade purity.
Important Research Notice
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY: All peptides and information provided are intended solely for laboratory research purposes. Products are not approved for human consumption, medical use, or diagnostic purposes. Research should be conducted by qualified personnel in appropriate laboratory settings with proper safety protocols.